Aspect Ratio: Why Does It Matter in Screen Size Calculations?
Do you wonder why some screens look wider or taller and why videos seem stretched or squeezed? The answer is the aspect ratio – how wide and tall a screen is. It affects how movies are framed and how comfortable watching videos on your phone is.
In this blog, let’s explore the most common types you will encounter and explain why they matter when choosing the right display for your needs.
The all-in-one solution for your AV needs
Transform your audio-visual experience with XTEN-AV.
No Credit Card required
Key Takeaways
- Learn that aspect ratio isn’t just a technical term; it directly shapes how content looks and feels on a screen.
- Discover how aspect ratio choices can enhance the visual impact and emotional resonance of your work.
- Armed with the understanding of aspect ratios, you will be able to select TVs, monitors, or mobile devices that can improve your viewing experience.
What is the Aspect Ratio?
In visual media, aspect ratio is important. This ratio represents screen size in an x:y or length and height format in TVs, monitors, or LED displays.
For example, the aspect ratio tells you how much wider a rectangle is compared to its height. A 16:9 TV screen ratio, common for TVs and monitors, means the screen is 16 units wide for every 9 units tall.
The aspect ratio isn’t about the actual size of the screen; it’s about its shape. This shape significantly influences how images and videos are displayed, impacting everything from your movie-watching experience to how you view photos on your phone.
What to know more about the history related to screen aspect ratios?
Nowadays, widescreen TV uses the 16:9 screen aspect ratio more than any other. However, this was not always the case.
The standard film format since the 1910s was the 4:3 TV screen ratio adopted by the Society of Motion Picture Engineers. In the 1930s, television also adopted this standard.
However, over time, the movie-making industry began creating cinemas in a wide-screen format, prompting television to change to 16:9.
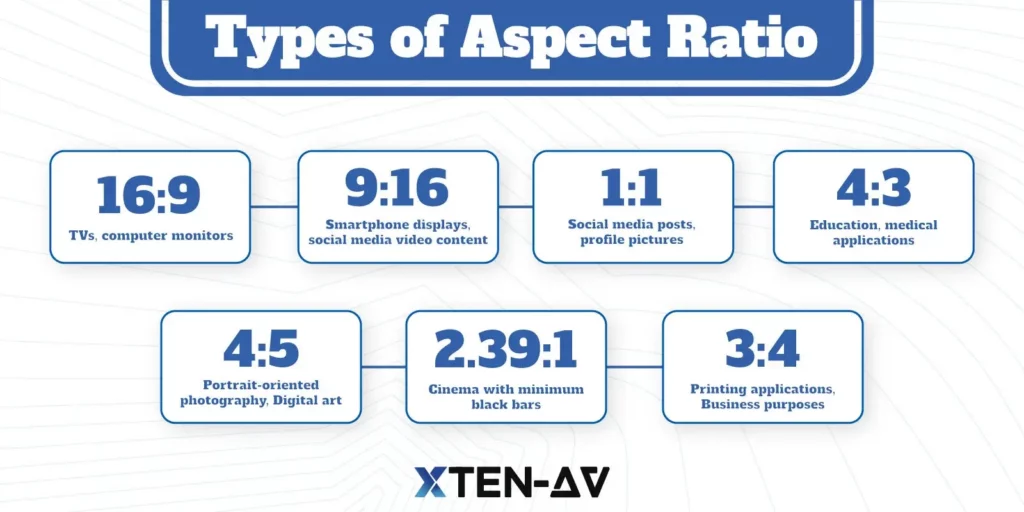
What are the common aspect ratios?
Below are some of the common aspect ratios in use today:
- 16:9 (Widescreen) – This aspect ratio is the standard for HDTVs, Blu-ray, YouTube, and almost every modern display like TVs, computer monitors, and smartphones.
- 9:16 (Portrait) – Smart phone displays and social media content such as Instagram posts and stories often make use of this portrait orientation display aspect ratio.
- 1:1 (Square) – Square 1:1 aspect ratio is popular with social media content such as Instagram posts, profile pictures and selected desktops or professional monitors.
- 4:3 (Standard) – This is a classic TV screen ratio used for old TV sets, computer screens, and video content. It is still used in a few educational applications and for medical purposes.
- 4:5 (Vertical) – Some portrait-oriented photography and digital art may be composed using 4 to 5.
- 2.39:1 (Cinema) – Sometimes called ultrawide, this ultra-wide TV screen ratio is found on certain high-end computer monitors suited for movies without much black bars.
- 3:4 (Business) – Some professional photography printing applications use a 3 by 4 ratio because it matches standard photographic film and paper sizes.
Where do we use the aspect ratio?
Aspect ratios are important for visual experiences, both at home and in the wider world:
Home Entertainment:
- Television and Projectors: The aspect ratio of your TV and projector screen impacts how movies, shows, and video games are displayed. The current standard is a widescreen 16:9 format, which offers a cinematic feel for most content.
- Home Theaters: When designing a home theater, the room’s dimensions, viewing distance, and the projector’s screen size aspect ratio should be considered to create the best viewing experience.
- Streaming and Online Video: Most online video content is optimized for 16:9 displays. Yet, vertical videos (9:16) are becoming a trend on social media platforms like TikTok and Instagram.
Personal Devices:
- Smartphones: The display aspect ratio of your phone screen affects how you view photos, videos, and apps. Newer phones often have taller aspect ratios (like 20:9) to accommodate more content.
- Tablets and Laptops: These devices typically have aspect ratios closer to 16:10 or 3:2, balancing screen space for productivity and media computation.
Digital Content Creation:
- Photography: The choice of aspect ratio depends on what a photographer wants to achieve (composition) and how photos will be used (intended use). Some popular ones include three over two, four over three, and square one.
- Video Production: An aspect ratio can dictate a video’s mood and style. Most directors choose either sixteen-nine or two-point-three nine-to-one (cinematic widescreen).
Commercial and Professional Settings:
- Digital Signage: Aspect ratios for digital signs are selected based on what content is being shown and at what distance it is viewed.
- Presentation: Consider the projector or screen you will use when making presentations because their display aspect ratios determine how your slides look.
- Medical Imaging: Specialized screen aspect ratios are often used in medical displays designed to view X-rays, scans, and other diagnostic images.
Changing Aspect Ratios: A Word of Caution
It’s essential to be careful while many gadgets are adaptable to aspect ratio adjustment:
- Deformation: Changing the TV screen ratio might result in image or video distortion, making them look like they have been stretched or compressed. This is especially evident in faces or things that should appear naturally.
- Missing Details: Occasionally, changing the aspect ratio of an image or a video may cause some parts to be cropped, resulting in the loss of visual information.
- Inconsistent Experience: If you change the aspect ratio on one device, the content may not display correctly on other devices with different ratios. This can ruin your viewing experience completely.
When to change an aspect ratio?
Here are times when you should change an aspect ratio:
- Filling the Screen: If a video or image does not fit your screen perfectly, adjusting the aspect ratio can sometimes be useful to fill the entire display area.
- Artistic Intent: In creative fields like photography and filmmaking, intentionally altering the aspect ratio can be used for artistic purposes to kindle specific emotions or create visual styles.
Aspect Ratio VS Resolution: Know the Difference Between
Features | Aspect ratio | Resolution |
Definition | Proportional relation between the width and height of a screen | The number of pixels (dots) that make up an angle |
How is it represented | Two numbers separated by a colon (example 16:9 or 4:3) | Width * height ( example 1920 * 1080, 3840 * 2160) |
What it affects | The shape of the screen | The level of detail and clarity of an image or video |
Analogy | Like the dimensions of the frame | Like the threads in a piece of fabric. More threads = Better quality or detail |
Relationship | Aspect ratio and resolution are independent of each other | Higher resolutions can be displayed on screens with any aspect ratio |
What is the importance of aspect ratio in screen size Calculations?
When choosing the perfect screen size, understanding the display aspect ratio is important. So why are TV screen ratios important in screen size resolutions?
Screen size calculators factor in aspect ratio because it directly impacts:
- Viewing distance: A wider screen might require you to sit further away from the screen size and aspect ratio to view the visual perfectly.
- Content compatibility: The aspect ratio of your screen should match the content you plan to view. Watching the widescreen movies on a 4:3 screen will result in black bars on the top and bottom. On the other hand, watching a 4:3 on a widescreen TV can stretch or distort the visual.
- Room measurements: The size and shape of your av room matter when selecting a screen with the right size and aspect ratio. A larger screen can engulf a small room, whereas smaller display sizes can be underwhelming when placed in bigger rooms.
XTEN-AV Screen Size Calculator: The perfect answer for your Aspect Ratio
Sometimes, manual calculations of aspect ratios can also be tiresome. However, there is no need for that! With a free XTEN-AV screen size calculator, like XTEN-AV’s calculator, you can easily do all these calculations without any problem. In addition, it has other advantageous features.
Here’s why you should try out XTEN-AV’s Free Screen Size Calculator:
DISCAS recommendation: XTEN-AV’s calculator sticks to the display image size for 2D content in Audiovisual Systems, ensuring optimal viewing experience.
Ideal screen size: XTEN-AV examines your room dimensions and viewing distance and recommends the perfect screen size for your specific environment.
Enhanced visuals: The calculator ensures the screen area and aspect ratio are perfect for maximum visual impact and clarity.
Customizable: You can customize the screen size to your specific purpose, such as home theater, presentations, or digital signage.
How does the XTEN-AV Screen Size Calculator work?
XTEN-AV’s free screen size calculator uses aspect ratio and other factors to determine the ideal screen size. Our formula is based on AV designs as per the AVIXA standards:
D = sqrt(W^2 + H^2)
W = AR * Image height
H = L / Discas Constant * Image height
Where:
D = Diagonal Screen Size
W = Width of the Screen
H = Height of the Screen
AR = Aspect Ratio
L = Distance of the last person viewing the display
AV Design Mastery + Winning Proposals = 10x Productivity!
- Automatic Cable Labeling & Styling
- 100+ Free Proposal Templates
- Upload & Create Floor Plans
- 1.5M Products from 5200 Brands
- AI-powered ‘Search Sense'
- Legally Binding Digital Signatures
Influence Your Viewing Experience Today
Knowing aspect ratios can help you understand which display best suits your needs. Make sure to consider factors and the optimal viewing experience before you select the perfect screen.
If you still have difficulty finding the perfect screen size for your space, check out XTEN-AV Screen Size Calculators. With this, discover how aspect ratio, viewing distance, and room dimensions combine to create an enjoyable visual experience.
FAQs
Another name for the 2.39: 1 display aspect ratio is “anamorphic widescreen” or “CinemaScope.” This can be achieved by cropping the height of the image. In this way, it employs most of the possible film frame or sensor area. On the other hand, increasing its width would mean that one would have to use a larger film or sensor, which is more expensive and rare. Furthermore, reducing the height keeps the horizontal field of view but creates a wider and more immersive picture with no difference in content composition.
The 2.39:1 screen aspect ratio is considered the most cinematic due to its wider view angle, which suggests grandeur and immersion, hence making it popular in epic films, action movies, and other genres that want a cinematic look.
Sensor size refers to the physical dimensions of an image sensor found inside a camera or any other imaging device. Bigger sensors capture more light, leading to better-quality images. On the other hand, the TV screen ratio represents the proportional relationship between the width and height of an image, regardless of its sensor size.
Aspect ratio in audiovisual technology refers to the relative relationship between the screen’s width and height. This determines its shape and may influence the perceived size or impact of the presentation.
This 2.39:1 display aspect ratio is also called CinemaScope or anamorphic widescreen. It mostly happens when image height is cut-off since it takes full advantage of the available film or sensor area. To make this wider, bigger films or sensors would have to be used, which are more expensive and less common. For instance, you cannot convert a TV screen that is 55 inches into an TV screen ratio because screen size measures diagonally while the TV screen ratio explains how wide a picture is compared to its height.
There are a few ways to find the TV screen ratio of a screen:
- Inspect device specs- These are usually found in user manuals or online.
- Take measurements of your screen – Obtain dimensions of what can be seen on the screen. First, measure width and then length. Finally, divide length by width (e.g., 16:9), simplifying if possible.
- Use online calculators- There are several web-based tools that will calculate TV screen ratios using dimensions of screens as entered by users.